报告详情
印度尼西亚绿色葡萄状玉髓的宝石学特征与颜色成因
编号:8
访问权限:仅限参会人
更新:2021-10-28 17:07:39
浏览:835次
张贴报告
摘要
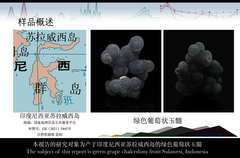
摘要:产于印度尼西亚的葡萄状玉髓,由粒度2~5mm的球粒状SiO2多晶集合体呈簇状形成,通常呈浅绿~深绿色、蓝绿色、紫色或紫-绿色混杂,具有独特的外观,是良好的宝石及观赏石材料。目前对葡萄状玉髓的结构及颜色成因的研究较少,本文针对葡萄状玉髓中绿色的品种对其宝石学特征于颜色成因展开研究。结合偏光显微镜及扫描电镜(SEM)对双面抛光片、岩石薄片以及新鲜断口的观察,表明该球粒状玉髓具有放射状“核心”——微晶石英过渡带——巨晶石英外壳的特殊壳层结构,隐晶质部分主要由粒度小于1mm的形状不规则的SiO2颗粒组成。
通过激光拉曼光谱(Raman)、X射线粉晶衍射(XRD)以及电子探针(EPMA)对其内部杂质矿物进行研究,发现玉髓主要由a-石英、斜硅石组成,含有少量黄铁矿、碳酸钙、以及磷铝质/钙磷质杂质矿物。通过计算斜硅石(503cm-1)和a-石英(464cm-1)拉曼位移的主峰强度比值I(503)/I(465) [%],认为斜硅石含量约为0~60wt.%,与玉髓的生长环境及地质成因有关,但与其绿色无关。绿色主要由绿色杂质矿物产生,部分绿色杂质矿物呈絮状,边缘模糊且结构松散,呈鲜绿色,多富集于玉髓裂隙及球粒之间的空隙中。另一部分绿色杂质矿物则呈现环带状混杂于玉髓中,呈深绿~黄褐色,背散射电子图像下表现为较高衬度且边界清晰,EPMA表明该矿物具有较高的P2O5(28wt.%)和CaO(48wt.%)成分。而XRD分析则表明玉髓主要由a-石英、斜硅石以及Al-PO4三种物相组成,其中Al-PO4及有可能与玉髓的绿色有关。
关键词:绿色玉髓;结构特征;杂质矿物致色;电子探针;X射线粉晶衍射
Abstract: Grape chalcedony produced in Indonesia is formed by SiO2 sphere which is polycrystalline aggregates with size of 2-5 mm. It is usually light to dark green, bluish-green, purple, or purple-green mixed. It is its unique appearance make it become an excellent gemstone and ornamental stone material. At present, there are few research on the structure and color origin of grape chalcedony. In this paper, the gemological characteristics and color origin of green grape chalcedony are studied. Observe the double-sided polished section, petrographic thin sections and fresh fracture by polarizing microscope and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which indicate the grape chalcedony has the special core-shell structure of radial quartz forms the “core”, microcrystalline quartz forms transition zones, and giant crystalline quartz forms shell. The cryptocrystalline part is mainly composed of irregular SiO2 particles with particle size less than 1mm.
Raman spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) were used to study the impurity minerals in chalcedony. It was found that chalcedony is mainly composed of a-quartz and moganite, contain a little pyrite, CaCO3 and P-Al/Ca-P minerals. The content of moganite is estimated about 0 ~ 60wt.% by calculating the intensity ratio of their Raman shift, i.e. I(503)/I(465) [%], where (503cm-1) is the main peak of the moganite and (464cm-1) belongs to a-quartz. Moganite is related to the growing environment and geological origin of chalcedony but has nothing to do with its green color. Green is mainly produced by green impurity minerals, some of which are flocculent, fuzzy, and loose in structure, bright green, and mostly enriched in chalcedony fissure and interspaces between spherules. The other part of the green impurity minerals showed a ring band mixed in chalcedony, dark green to yellowish brown, with high contrast and clear boundary under the backscattering electron image. EPMA showed that the mineral had a high composition of P2O5 (28wt.%) and CaO (48wt.%). XRD analysis shows that chalcedony is mainly composed of a-quartz, moganite and Al-PO4, among which Al-PO4 may be related to the green color of chalcedony.
Key words: green chalcedony; structural characteristics; impurity mineral chromaticity; Electron probe microanalysis; X-ray powder diffraction
通过激光拉曼光谱(Raman)、X射线粉晶衍射(XRD)以及电子探针(EPMA)对其内部杂质矿物进行研究,发现玉髓主要由a-石英、斜硅石组成,含有少量黄铁矿、碳酸钙、以及磷铝质/钙磷质杂质矿物。通过计算斜硅石(503cm-1)和a-石英(464cm-1)拉曼位移的主峰强度比值I(503)/I(465) [%],认为斜硅石含量约为0~60wt.%,与玉髓的生长环境及地质成因有关,但与其绿色无关。绿色主要由绿色杂质矿物产生,部分绿色杂质矿物呈絮状,边缘模糊且结构松散,呈鲜绿色,多富集于玉髓裂隙及球粒之间的空隙中。另一部分绿色杂质矿物则呈现环带状混杂于玉髓中,呈深绿~黄褐色,背散射电子图像下表现为较高衬度且边界清晰,EPMA表明该矿物具有较高的P2O5(28wt.%)和CaO(48wt.%)成分。而XRD分析则表明玉髓主要由a-石英、斜硅石以及Al-PO4三种物相组成,其中Al-PO4及有可能与玉髓的绿色有关。
关键词:绿色玉髓;结构特征;杂质矿物致色;电子探针;X射线粉晶衍射
Abstract: Grape chalcedony produced in Indonesia is formed by SiO2 sphere which is polycrystalline aggregates with size of 2-5 mm. It is usually light to dark green, bluish-green, purple, or purple-green mixed. It is its unique appearance make it become an excellent gemstone and ornamental stone material. At present, there are few research on the structure and color origin of grape chalcedony. In this paper, the gemological characteristics and color origin of green grape chalcedony are studied. Observe the double-sided polished section, petrographic thin sections and fresh fracture by polarizing microscope and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which indicate the grape chalcedony has the special core-shell structure of radial quartz forms the “core”, microcrystalline quartz forms transition zones, and giant crystalline quartz forms shell. The cryptocrystalline part is mainly composed of irregular SiO2 particles with particle size less than 1mm.
Raman spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) were used to study the impurity minerals in chalcedony. It was found that chalcedony is mainly composed of a-quartz and moganite, contain a little pyrite, CaCO3 and P-Al/Ca-P minerals. The content of moganite is estimated about 0 ~ 60wt.% by calculating the intensity ratio of their Raman shift, i.e. I(503)/I(465) [%], where (503cm-1) is the main peak of the moganite and (464cm-1) belongs to a-quartz. Moganite is related to the growing environment and geological origin of chalcedony but has nothing to do with its green color. Green is mainly produced by green impurity minerals, some of which are flocculent, fuzzy, and loose in structure, bright green, and mostly enriched in chalcedony fissure and interspaces between spherules. The other part of the green impurity minerals showed a ring band mixed in chalcedony, dark green to yellowish brown, with high contrast and clear boundary under the backscattering electron image. EPMA showed that the mineral had a high composition of P2O5 (28wt.%) and CaO (48wt.%). XRD analysis shows that chalcedony is mainly composed of a-quartz, moganite and Al-PO4, among which Al-PO4 may be related to the green color of chalcedony.
Key words: green chalcedony; structural characteristics; impurity mineral chromaticity; Electron probe microanalysis; X-ray powder diffraction
关键词
绿色玉髓;结构特征;杂质矿物致色;电子探针;X射线粉晶衍射
报告人

LuoHeng
中国地质大学(武汉)稿件作者
全部评论
重要日期
-
会议日期
10月30日
2021
至10月31日
2021
-
10月31日 2021
初稿截稿日期
-
10月31日 2021
注册截止日期
主办单位
中国地质大学(武汉)珠宝学院
湖北省人文社科重点研究基地
湖北省人文社科重点研究基地
联系方式
- 珠宝学院
- gi******@cug.edu.cn
- 138********
历届会议
-
2022年10月30日 中国 武汉市
第三十届武汉国际珠宝学术年会暨第二届湖北省珠宝技术工程中心学术会议 -
2020年10月17日 中国 Wuhan
第二十八届武汉国际珠宝学术年会暨第一届湖北省珠宝技术工程中心学术会议 -
2019年11月02日 中国 Wuhan
2019 国际珠宝学术年会 -
2009年10月24日 中国 武汉市
2009珠宝学术年会


发表评论